Usually women obsess about their size, no matter health ramifications and these approaches persist when they fall pregnant. Society at large fears not thin, even during pregnancy. But a healthy weight gain plays a huge part in a healthy pregnancy.
On no account cut back on eating as it deprives you of results and great nourishment in a little, sickly baby experiencing constant health issues.
With nearly two thirds of women at childbearing age in the U.S. being overweight or fat, make sure you reduce your weight before you conceive.
How much weight should you gain during pregnancy? Begin with your Body Mass Index (BMI), a ratio between your height and weight in the time of conception and for most people a dependable index of their body fat.
You can search on Google, type: ‘BMI calculator’, choose one of the websites, establish metric or English, out pops your BMI, and put in your height and weight. Less than 18.5 are considered underweight, 18.5 to 24.9 standard, 25 to 29.9 overweight, and 30 plus fat.
As a reference, a 5-foot-6-inch woman weighing between 115 and 154 pounds is considered normal.
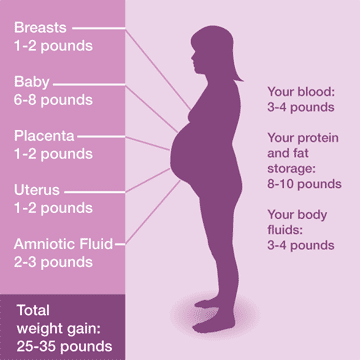
Recommended Weight Gain Guidelines during Pregnancy
Following these guidelines issued by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) in May 2009, lowers health risks for both moms as well as their babies.
In case you’re pre-pregnancy weight was in the healthy range for your height (a BMI of 18.5 to 24.9), you should gain between 25 and 35 pounds. In the first trimester your gain will be 4 or 3 pounds, partially water weight and partially materials to help your baby that is tiny grow. Afterwards gain 1 pound a week for the rest of your pregnancy to make sure optimal baby growth, a more comfortable pregnancy and also a safe delivery.
Underweight women (a BMI of below 18.5) may be less prolific due to their low body fat, but if you conceived, get a total of 28 to 40 pounds; 5 to 6 pounds in the first trimester and somewhat more than 1 pound a week for the second and third. If you were overweight for your height (a BMI of 25 to 29.9), get a total of 15 to 25 pounds; 2 to 3 pounds in the first trimester and marginally more than 1/2 pound per week for the second and third trimesters.
If you’re expecting twins, gain 37 to 54 pounds if you began at a healthy weight; 31 to 50 pounds if you were overweight; and 25 to 42 pounds if you were fat, gaining about 1 1/2 pounds a week in the second and third trimesters.
Some obstetricians and gynecologists want to see these bodies shift with women in the healthy range. The lower amounts are considered adequate for a healthy infant yet and were recommended in the 1970s additionally allow it to be simpler for women to return to their pre-pregnancy weight.
Chart your weight gains
In the event that you have problems with nausea and morning sickness in your first trimester, food might not interest you personally and any weight gain will probably be negligible. Not to stress. Later on in your pregnancy is when the baby that is growing particularly needs calories and nutrients for appropriate growth and by then your morning sickness will probably be long gone.
Toward the end of your pregnancy you may gain a bit more, stop, or even notice a negligible weight loss at the very end. Plus-sized women may really lose a small weight during their pregnancy and have reservations within their fat that is stored.
Restricting your food consumption and attempting to shed weight while anticipating is not recommended as the fat stores you burn may include materials dangerous to the baby. Gaining muscle is allowed; though first discuss exercising with your physician ahead.
In case you have one or two ‘growth spurts’ gaining several pounds over a brief period and then level off, do not be concerned.
But in the event you suddenly gain over five pounds per week during the 2nd half of your pregnancy, beware; this may be an indication of preeclampsia, both you as well as your baby threatening.
Get in touch with your doctor also in the event that you don’t gain weight for more than two weeks between the eighth and fourth month of your pregnancy.
How to stay within the recommended range
Eating healthily is right for the growing baby as well as you. Your physician will determine what makes up a wholesome weight gain for you. Your doctor will even prepare you as to what the best way to work out and to eat.
The old maxim ‘eating for two’ will not give free reign to eat twice what you usually do to you.
If your weight at conception falls in the standard range of BMI, during the first 12 weeks of your pregnancy you desire 100 to 200 extra calories a day; for the balance 200 to 300, with underweight women desiring 300 to 500 extra calories a day.
300 calories isn’t a lot. For instance, an extra snack of four fig bars as well as a glass of skim milk covers it.
Dangers of gaining too much weight or being overweight at conception
Although heavy women appreciate healthy pregnancies and deliver without complications, there are potential risks. You can miscarry, it cannot be easy assess the size of the uterus and to hear the baby’s pulse, and subsequent to the arrival you’ll find it almost impossible to slim down and most likely will weigh more in later pregnancies. You threat complications like gestational diabetes, high blood pressure and preeclampsia. Your infant might be too large at birth, making vaginal delivery agonizing and long, raising the chances of you needing a cesarean delivery, as well as the child will most likely become overweight or fat himself. Also you’ll most likely have difficulty breastfeeding, partially due to poor milk production and partly because you find it almost impossible to place the baby for nursing.
Medical tests like ultrasounds to assess the size of your baby and a glucose tolerance test to screen for gestational diabetes might be proposed during your pregnancy, in order to lower your risks.
Dangers of gaining too little weight
People who start pregnancy underweight or who do not gain enough during pregnancy, danger stunted fetal growth, delivering a low-birth-weight baby weighing less than 5.5 pounds, and preterm delivery which can cause severe health problems for the infant, even death, if birth is too premature.
Obeying these guidelines
Women are strongly advised to comply with these recommended weight gains. True your metabolism, activity level and genetics play a part, but with routine visits to your doctor, you both can ensure your pregnancy progresses smoothly.
Gaining weight slowly means your baby has a steady supply of nutriments, a few of which are stored for breastfeeding, lowering your chances of stretch marks, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, backache, fatigue, indigestion, and shortness of breath during pregnancy.
Guidelines to gain healthy weight
Eat five to six small meals a day consisting of nutrient dense food which nourishes your infant as well as you. Seek foods like cheese, vegetables, nuts, dried fruit, peanut butter, yogurt, fresh fruit, whole grains, lean protein, oily fish, and dairy products. Limitation junk food, candy, biscuits, donuts, cake, pie, potato chips coffee and pop, loaded with calories but no nourishment. Prevent alcohol and smoking.
In the event that you should gain weight quicker, add butter, cream cheese and sour cream to nonfat powdered milk to mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs and hot cereal, and meals.
What to do if you need to slow down your weight gain during pregnancy
Rather than limiting your eating, make more healthy selections. Replace high calorie fried whole milk products and foods with foods mentioned previously and you’ll feel satiated. Restrict beverage water, club soda or diluted fresh fruit juice and sweetened beverages rather.
Routine moderate exercise, like walking, yoga or swimming, is powerful both during your pregnancy and your baby is born.
You have to tread a fine line between consuming extra calories, slowly gaining weight, and remaining effective without burning them all.
If you feel anxious about your increasing weight
If before you attentively observed your weight, you may not feel comfortable seeing it creep. Remind yourself that some weight gain is vital for a healthy pregnancy and will vanish after the arrival.
Losing those extra pounds after you give birth
A 25 pound weight gain during your pregnancy is spread in the following way: the infant 7.5 pounds, amniotic fluid 2.0 pounds, placenta 1.0 pound, breast tissue 1.5 pounds, uterus increase 2.0 pounds, additional blood supply 3.0 pounds, retained water 2.0 pounds, and protein and fat stores for delivery and breastfeeding 6.0 pounds.
You’ll lose roughly half your pregnancy weight in the first six weeks after delivery. The remainder took nine months to put on so allow that amount of time. Do so by eating healthily and exercising sensibly and it may come off sooner.
Do not dramatically reduce your calorie intake in an effort to boost your weight reduction since you desire energy to cope with being the mother of a newborn baby. When you breastfeed weight comes off faster because you burn 1000 to 1500 calories a day creating milk.
Exercise also plays a useful part following your baby’s arrival. It raises your self esteem and enables you to slim down, builds muscle, become more flexible, relieves depression.
Remember there is a pregnancy about taking a baby that is growing inside you, a real wonder of nature. Eating the proper quantity of quality food rewards you with not only a healthy baby, but also rapid weight reduction following the birth.
image : pinterest.com
Article publié pour la première fois le 24/08/2015
